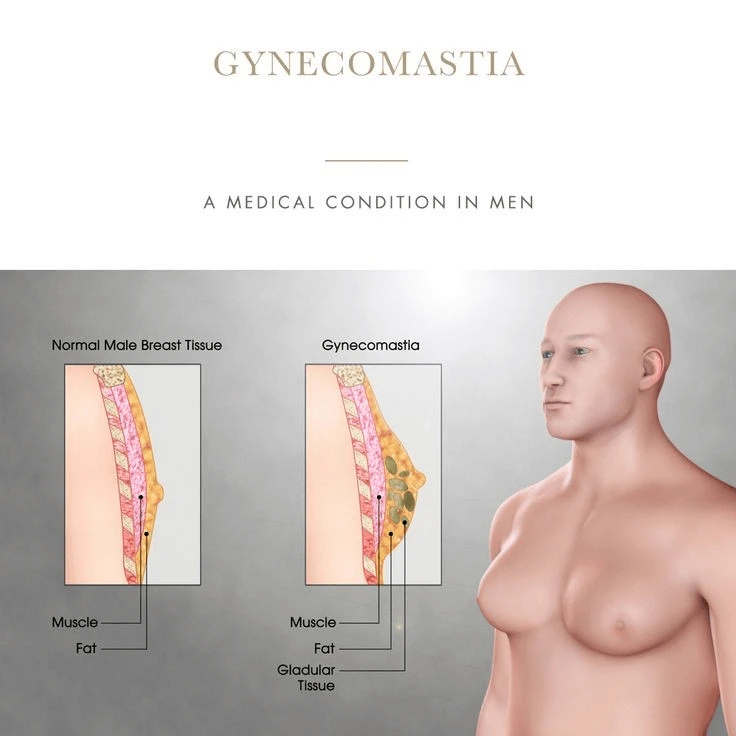
Male breast enlargement, known as gynecomastia, is a common condition that affects men of all ages. It occurs when an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen leads to the growth of glandular breast tissue. While often harmless, gynecomastia can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress, affecting self-confidence and quality of life.
Hormonal fluctuations play a major role in this condition. Factors such as puberty, aging, obesity, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, leading to excessive breast tissue growth in men. Understanding how hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and prolactin influence male breast development is key to identifying the causes and finding the right treatment options.
In this article, we will explore the hormonal causes of male breast enlargement, the impact of hormonal imbalances, available treatment options, and ways to prevent this condition. Whether you’re experiencing gynecomastia yourself or seeking information for someone else, this guide will provide valuable insights into managing and treating male breast growth effectively
What Causes Male Breast Enlargement?

Testosterone and Estrogen Imbalance – How Low Testosterone and High Estrogen Contribute to Gynecomastia
Hormonal balance is essential for maintaining male physical characteristics, including muscle mass, body hair, and a firm chest. Testosterone and estrogen are the two primary hormones that regulate male and female traits. While men naturally produce small amounts of estrogen, their testosterone levels typically keep it in check. However, when testosterone levels drop or estrogen levels rise abnormally, it can lead to gynecomastia, or male breast enlargement.
1. The Role of Testosterone in Preventing Breast Growth
Testosterone is the dominant male sex hormone, responsible for maintaining muscle tone, reducing fat accumulation in the chest, and inhibiting breast tissue development. When testosterone levels are low, there is less resistance against the effects of estrogen, allowing breast tissue to grow. Low testosterone can result from:
- Aging: As men age, testosterone production naturally declines, increasing the risk of hormonal imbalances.
- Hypogonadism: A medical condition where the testes produce little or no testosterone.
- Chronic Illnesses: Conditions like liver disease, kidney disease, and diabetes can interfere with testosterone production.
- Obesity: Excess body fat leads to higher estrogen levels, which can suppress testosterone production.
2. The Impact of High Estrogen on Male Breast Growth
Estrogen is commonly associated with female reproductive health, but men also produce small amounts for various bodily functions. However, elevated estrogen levels in men can directly stimulate breast tissue growth. Factors that contribute to high estrogen include:
- Increased Aromatase Activity: Aromatase is an enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen. Higher body fat levels increase aromatase activity, leading to excessive estrogen production.
- Liver Dysfunction: The liver plays a key role in metabolizing estrogen. Liver diseases like cirrhosis or fatty liver disease can result in estrogen buildup.
- Endocrine Disorders: Conditions affecting the endocrine system, such as thyroid imbalances or pituitary gland disorders, can trigger high estrogen levels.
- Medications and Environmental Estrogens: Certain drugs (e.g., anti-androgens, anabolic steroids, and some antidepressants) and exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (like BPA in plastics) can raise estrogen levels.
3. The Testosterone-Estrogen Ratio: Why Balance Matters
It’s not just the absolute levels of testosterone or estrogen that matter, but rather their ratio. When testosterone declines or estrogen increases, the imbalance tips in favor of estrogen, leading to breast tissue stimulation. This is why gynecomastia is common in older men, obese individuals, and those undergoing hormone therapy.
To prevent and manage gynecomastia, addressing the root cause of hormonal imbalance is crucial. Lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and hormonal therapies can help restore balance and reduce symptoms. In the next section, we’ll explore how hormonal imbalances impact male breast growth and potential treatment options.
Role of the Endocrine System – How Hormone Regulation Affects Breast Tissue Growth
The endocrine system is responsible for producing and regulating hormones that control various bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and sexual development. When this system is functioning properly, it maintains a delicate balance between testosterone and estrogen in men. However, disruptions in hormone production, metabolism, or signaling can lead to gynecomastia, or abnormal breast tissue growth in men.
Understanding the role of key endocrine glands and their impact on hormone regulation is crucial in identifying the underlying causes of male breast enlargement.
1. The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland: The Master Controllers of Hormones
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland, located in the brain, act as the control center for hormone regulation. They send signals to other endocrine glands, instructing them to produce the necessary hormones.
- The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which tells the pituitary gland to stimulate testosterone production.
- The pituitary gland produces luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which signal the testes to produce testosterone.
- If there is a dysfunction in either of these glands, testosterone production can decline, leading to an imbalance where estrogen becomes more dominant, contributing to gynecomastia.
Common conditions that affect these glands:
- Pituitary tumors or disorders – Can reduce testosterone production and increase prolactin, leading to breast growth.
- Hypogonadism – A condition where the testes don’t produce enough testosterone due to pituitary dysfunction.
- Head trauma or brain surgery – Can affect the function of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
2. The Testes: The Primary Source of Testosterone
The testes are the main producers of testosterone in men. If their function is impaired, it can lead to low testosterone levels, which allows estrogen to have a stronger effect on breast tissue.
Factors that can disrupt testosterone production include:
- Aging – Testosterone naturally declines with age, leading to an increased risk of hormonal imbalance.
- Injury to the testes – Physical trauma or medical conditions affecting the testes can reduce testosterone output.
- Chronic medical conditions – Diseases like diabetes and kidney failure can interfere with normal testicular function.
- Use of anabolic steroids – Misuse of steroids can cause the body to shut down natural testosterone production, leading to excess estrogen and gynecomastia.
When testosterone levels drop, estrogen’s effect on breast tissue increases, causing abnormal development.
3. The Liver and Adrenal Glands: Managing Estrogen Levels
The liver and adrenal glands also play significant roles in hormone metabolism and estrogen regulation.
Liver Function and Estrogen Metabolism
The liver is responsible for breaking down excess estrogen and removing it from the body. If liver function is compromised, estrogen levels can rise, increasing the risk of male breast enlargement.
Liver-related causes of high estrogen levels:
- Cirrhosis and fatty liver disease – Reduce the liver’s ability to metabolize estrogen efficiently.
- Excess alcohol consumption – Can impair liver function and promote estrogen buildup.
- Hepatitis and liver infections – Affect hormone metabolism and can contribute to hormonal imbalances.
The Adrenal Glands and Estrogen Production
The adrenal glands, located above the kidneys, produce small amounts of estrogen in men. If these glands become overactive, they can increase estrogen production, further disrupting the testosterone-estrogen balance.
Common adrenal-related causes of gynecomastia:
- Adrenal tumors – Can lead to excess estrogen production.
- Cushing’s syndrome – A condition where the adrenal glands produce too much cortisol, indirectly affecting testosterone levels.
- Chronic stress – Increases cortisol, which can suppress testosterone production and lead to an estrogen-dominant state.
How Endocrine Disorders Contribute to Male Breast Growth
When any part of the endocrine system is dysfunctional, it can lead to a hormonal imbalance that promotes breast tissue growth. Some endocrine disorders commonly linked to gynecomastia include:
- Hyperthyroidism – Overactive thyroid function can lead to increased estrogen activity in men.
- Hypogonadism – Low testosterone production due to underactive testes or pituitary dysfunction.
- Andropause (Male Menopause) – A natural decline in testosterone as men age, leading to an imbalance with estrogen.
Final Thoughts
The endocrine system plays a vital role in regulating testosterone and estrogen levels, both of which directly impact male breast tissue growth. Disruptions in the pituitary gland, testes, liver, and adrenal glands can all contribute to gynecomastia by altering hormone production and metabolism.
By identifying underlying endocrine issues, men can take proactive steps to balance their hormones through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or hormone therapy. In the next section, we will explore treatment options to manage and reduce male breast enlargement caused by hormonal imbalances
Medical Conditions That Affect Hormones – Hypogonadism, Liver Disease, and Obesity as Contributing Factors
Hormonal imbalances that lead to male breast enlargement (gynecomastia) can be caused by several underlying medical conditions. These conditions disrupt the natural balance between testosterone and estrogen, allowing breast tissue to grow in men. Three of the most common medical conditions that contribute to hormonal imbalances and gynecomastia are hypogonadism, liver disease, and obesity.
Each of these conditions affects hormone production, metabolism, or regulation, leading to an increased estrogen-to-testosterone ratio, which stimulates breast tissue development. Understanding these medical factors can help in identifying the root cause of gynecomastia and guide appropriate treatment strategies.
1. Hypogonadism: Low Testosterone Production and Its Impact on Gynecomastia
Hypogonadism is a condition in which the testes fail to produce sufficient testosterone, leading to an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen. Since testosterone plays a crucial role in inhibiting breast tissue growth, low levels allow estrogen to become more dominant, increasing the risk of male breast enlargement.
Types of Hypogonadism
There are two primary types of hypogonadism:
- Primary Hypogonadism: The testes themselves are dysfunctional and cannot produce enough testosterone.
- Secondary Hypogonadism: The problem lies in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, which fails to signal the testes to produce testosterone.
Causes of Hypogonadism
- Genetic conditions like Klinefelter syndrome (XXY chromosomes) cause low testosterone and gynecomastia.
- Aging-related testosterone decline (andropause) naturally lowers testosterone over time.
- Testicular injuries or infections (e.g., mumps orchitis) can impair testosterone production.
- Pituitary gland disorders reduce the signaling for testosterone production.
How Hypogonadism Contributes to Gynecomastia
When testosterone levels drop, estrogen’s effects become more pronounced, leading to:
✔ Increased breast tissue growth
✔ Fat accumulation in the chest area
✔ Loss of muscle mass, allowing fat to replace lean tissue
✔ Reduced libido and energy levels
Treatment for Hypogonadism-Related Gynecomastia
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) – Helps restore hormonal balance and may reduce breast tissue.
- Clomiphene Citrate or Aromatase Inhibitors – Can help stimulate testosterone production and block estrogen.
- Lifestyle Modifications – Proper diet and exercise to enhance natural testosterone production.
2. Liver Disease: How Poor Liver Function Leads to Excess Estrogen
The liver plays a key role in hormone metabolism, including the breakdown and elimination of excess estrogen from the body. When liver function is impaired, estrogen levels can build up, leading to hormonal imbalances that promote gynecomastia.
Liver Conditions That Affect Hormonal Balance
- Cirrhosis – Chronic liver damage leads to decreased estrogen metabolism, causing estrogen buildup.
- Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) – Excess fat in the liver reduces its efficiency in hormone regulation.
- Hepatitis and Chronic Liver Inflammation – These conditions impair liver function and hormonal clearance.
How Liver Disease Causes Male Breast Enlargement
✔ Reduced estrogen metabolism → Higher estrogen levels stimulate breast tissue growth.
✔ Low production of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) → Increases free estrogen in the bloodstream.
✔ Altered testosterone metabolism → The liver also helps regulate testosterone levels, and liver disease may lower testosterone production.
Signs of Liver-Related Gynecomastia
- Enlarged male breast tissue
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal bloating and fluid retention
- Unexplained weight gain or muscle loss
Treatment for Liver Disease-Related Gynecomastia
- Improving liver health through diet and lifestyle changes (reducing alcohol, processed foods, and sugar).
- Medications to manage liver disease and reduce hormonal imbalances.
- Estrogen-lowering drugs like Tamoxifen or Aromatase Inhibitors (for severe cases).
3. Obesity: The Link Between Excess Fat, Estrogen Production, and Gynecomastia
Obesity is one of the most common causes of gynecomastia because excess body fat increases estrogen levels while simultaneously reducing testosterone production. Fat cells contain an enzyme called aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen. The more fat a person has, the more testosterone gets converted to estrogen, leading to male breast enlargement.
How Obesity Contributes to Gynecomastia
✔ Excess fat = More aromatase activity → Leads to higher estrogen levels.
✔ Higher estrogen levels = Increased breast tissue growth.
✔ Lower testosterone production → Fat accumulation in the chest, making it harder to maintain a masculine physique.
✔ Inflammation and insulin resistance → Chronic inflammation further disrupts hormone balance.
Visceral vs. Subcutaneous Fat and Hormones
- Visceral fat (deep abdominal fat) is strongly linked to hormonal imbalances and increased estrogen production.
- Subcutaneous fat (just under the skin) contributes to chest fat accumulation, making gynecomastia appear more severe.
Treatment for Obesity-Related Gynecomastia
- Weight loss through diet and exercise – Helps reduce aromatase activity and lowers estrogen production.
- Strength training and resistance exercises – Boost testosterone levels naturally.
- Intermittent fasting and low-carb diets – Help regulate insulin and hormone balance.
- Medical interventions (if needed) – In extreme cases, doctors may recommend hormone therapy or surgery.
Final Thoughts
Medical conditions like hypogonadism, liver disease, and obesity significantly contribute to hormonal imbalances, leading to male breast enlargement. Each of these conditions either reduces testosterone production, increases estrogen levels, or disrupts hormone metabolism, allowing breast tissue to grow abnormally.
Understanding these underlying causes can help men take the right steps toward balancing their hormones through lifestyle changes, medical treatments, or hormone therapy.
In the next section, we will explore treatment options for gynecomastia, including natural remedies, medical therapies, and surgical procedures to help men regain confidence and a balanced hormonal profile.
Hormonal Imbalances and Their Impact on Male Breast Growth

The Role of Estrogen and Prolactin – How Excess Estrogen and Prolactin Lead to Breast Tissue Development
Male breast enlargement, or gynecomastia, is primarily driven by hormonal imbalances that affect breast tissue growth. While testosterone helps maintain masculine traits, an excess of estrogen and prolactin can lead to abnormal breast tissue development in men.
- Estrogen is the primary female sex hormone, but men also produce small amounts. When estrogen levels become too high, it stimulates breast tissue growth, leading to gynecomastia.
- Prolactin is the hormone responsible for breast development and milk production in women. Although prolactin levels are typically low in men, certain medical conditions, medications, or tumors can increase its levels, contributing to male breast enlargement.
This section will explore how elevated estrogen and prolactin contribute to gynecomastia and what factors cause their imbalances.
1. Estrogen: The Key Hormone Behind Male Breast Growth
Estrogen plays a significant role in breast tissue development. While it is primarily a female hormone, men naturally produce small amounts to support brain function, bone health, and cardiovascular health. However, when estrogen levels rise too high, it can directly stimulate the growth of glandular breast tissue, leading to male breast enlargement.
How Estrogen Stimulates Breast Tissue in Men
✔ Promotes breast tissue development → Estrogen stimulates mammary gland growth.
✔ Suppresses testosterone production → Higher estrogen levels reduce testosterone, making it harder to prevent breast growth.
✔ Increases fat accumulation → Estrogen encourages fat storage, especially in the chest area, making gynecomastia appear more pronounced.
Causes of High Estrogen in Men
Several factors can increase estrogen levels, leading to hormonal imbalances and breast tissue growth:
1. Increased Aromatase Activity (Testosterone to Estrogen Conversion)
Aromatase is an enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen.
- Excess body fat increases aromatase activity, leading to higher estrogen levels.
- Aging naturally increases aromatase activity, making older men more prone to gynecomastia.
2. Liver Dysfunction (Reduced Estrogen Metabolism)
The liver helps regulate estrogen levels by breaking down and removing excess estrogen.
- Liver diseases like cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, or hepatitis can impair this process, causing estrogen levels to rise.
- Chronic alcohol consumption can also reduce the liver’s ability to metabolize estrogen properly.
3. Endocrine Disruptors (Environmental Estrogens)
- Plastics containing BPA (Bisphenol A) can mimic estrogen in the body.
- Pesticides and industrial chemicals can act as endocrine disruptors, increasing estrogen levels.
4. Medications That Increase Estrogen Levels
Certain medications can directly or indirectly raise estrogen levels, leading to gynecomastia:
- Anabolic steroids – Convert into estrogen after being metabolized.
- Anti-androgens (e.g., finasteride, spironolactone) – Block testosterone, allowing estrogen to dominate.
- Certain heart medications and antidepressants can also contribute to hormonal imbalances.
Signs of High Estrogen in Men
Men with elevated estrogen may experience:
✔ Male breast enlargement (glandular tissue growth)
✔ Increased body fat, especially around the chest and abdomen
✔ Low libido and erectile dysfunction
✔ Mood swings, depression, or anxiety
✔ Fatigue and lack of energy
2. Prolactin: The Hormone That Stimulates Breast Tissue Growth
Prolactin is a hormone mainly associated with breast development and milk production in women. However, men also produce small amounts for various bodily functions.
When prolactin levels rise too high in men, it can stimulate breast tissue growth, leading to gynecomastia. Unlike estrogen, prolactin not only increases breast size but may also cause nipple discharge (galactorrhea) in some cases.
How Prolactin Affects Male Breast Growth
✔ Promotes mammary gland enlargement – Excess prolactin leads to the growth of milk-producing glands, contributing to gynecomastia.
✔ Suppresses testosterone production – High prolactin levels inhibit gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which reduces testosterone levels.
✔ Affects dopamine levels – Dopamine helps regulate prolactin; when dopamine levels drop, prolactin levels increase, leading to hormonal imbalances.
Causes of High Prolactin in Men
1. Pituitary Gland Tumors (Prolactinomas)
- The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, regulates hormone production.
- A prolactinoma (pituitary tumor) can cause excessive prolactin production, leading to gynecomastia.
2. Medications That Increase Prolactin
Certain drugs can raise prolactin levels, leading to male breast enlargement:
- Antipsychotics (e.g., risperidone, haloperidol)
- Antidepressants (SSRIs, tricyclics)
- Opioids and painkillers
- Blood pressure medications (verapamil, methyldopa)
3. Chronic Stress and Lack of Sleep
- Stress increases cortisol, which can indirectly boost prolactin levels.
- Poor sleep quality disrupts dopamine, allowing prolactin to rise.
Signs of High Prolactin in Men
Men with elevated prolactin levels may experience:
✔ Breast tissue enlargement (with possible tenderness)
✔ Reduced libido and erectile dysfunction
✔ Loss of body hair and decreased muscle mass
✔ Fatigue and mood changes
✔ Possible nipple discharge (in rare cases)
3. The Combined Effect of High Estrogen and High Prolactin on Male Breast Growth
When both estrogen and prolactin levels are elevated, the risk of gynecomastia becomes much higher.
- Estrogen directly stimulates breast tissue growth, while
- Prolactin enhances glandular development, making the breast tissue denser.
This combination can result in:
✔ More pronounced breast enlargement (not just fat accumulation but glandular tissue growth)
✔ Breast tenderness or pain
✔ Increased nipple sensitivity
4. Treatment Options for Hormonal Imbalance-Related Gynecomastia
To reduce gynecomastia caused by high estrogen or prolactin, the following treatments may help:
1. Natural Ways to Lower Estrogen and Prolactin
- Weight loss and strength training – Reduces body fat and aromatase activity, lowering estrogen.
- Cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, kale) – Contain DIM (Diindolylmethane), which helps metabolize excess estrogen.
- Manage stress and improve sleep – Helps regulate dopamine and prolactin levels.
2. Medications for Hormonal Balance
- Aromatase inhibitors (Anastrozole, Letrozole) – Block estrogen production.
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) (Tamoxifen, Raloxifene) – Block estrogen’s effect on breast tissue.
- Dopamine agonists (Cabergoline, Bromocriptine) – Lower prolactin levels.
3. Medical Interventions
- Treat underlying conditions (e.g., remove pituitary tumors if prolactinoma is present).
- Surgery (Mastectomy or Liposuction) – For severe gynecomastia cases.
Final Thoughts
Excess estrogen and prolactin are major hormonal drivers of gynecomastia. High estrogen stimulates breast tissue growth, while high prolactin promotes glandular development. Understanding and addressing these hormonal imbalances through lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions can help reduce male breast enlargement and restore hormonal balance
Aromatase and Testosterone Conversion – The Enzyme That Converts Testosterone to Estrogen
One of the key factors contributing to gynecomastia (male breast enlargement) is the conversion of testosterone into estrogen through an enzyme called aromatase. This process, known as aromatization, can lead to an excess of estrogen in men, which in turn stimulates breast tissue growth.
Understanding how aromatase functions, what factors increase its activity, and how to reduce its effects is essential for managing hormonal imbalances and preventing gynecomastia.
1. What Is Aromatase?
Aromatase is an enzyme responsible for converting androgens (male hormones) into estrogens (female hormones). It plays a crucial role in hormonal balance and is naturally present in various tissues, including:
✔ Fat tissue (adipose tissue)
✔ Testes and adrenal glands
✔ Brain, liver, and muscles
While aromatase is necessary for normal estrogen production, excess aromatase activity can lead to high estrogen levels, disrupting the testosterone-to-estrogen ratio and increasing the risk of gynecomastia.
2. How Aromatase Converts Testosterone to Estrogen
The aromatase enzyme catalyzes the conversion of testosterone (T) and androstenedione (another androgen) into estradiol (E2) and estrone (E1), the two primary forms of estrogen in the body.
The Aromatase Reaction:
- Testosterone → Estradiol (E2) (active estrogen)
- Androstenedione → Estrone (E1) (weaker estrogen, can be converted into E2)
As aromatase activity increases, more testosterone is converted into estrogen, leading to higher estrogen levels and a reduction in free testosterone, which can contribute to gynecomastia, fat gain, and loss of muscle mass in men.
3. Factors That Increase Aromatase Activity
1. Excess Body Fat (Obesity and Aromatization)
✔ Fat cells contain high amounts of aromatase, making obesity a major risk factor for increased estrogen levels in men.
✔ More fat tissue means more aromatase activity, leading to higher estrogen production and a greater likelihood of gynecomastia.
✔ Abdominal and visceral fat produce the most aromatase, which is why overweight men often experience hormonal imbalances.
2. Aging and Natural Testosterone Decline
✔ As men age, testosterone levels naturally decline, while aromatase activity increases.
✔ Older men often experience higher estrogen-to-testosterone ratios, increasing the likelihood of gynecomastia, lower libido, and muscle loss.
3. Liver Dysfunction and Estrogen Clearance
✔ The liver plays a key role in metabolizing and removing excess estrogen.
✔ Conditions like fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, or chronic alcohol consumption impair the liver’s ability to break down estrogen, allowing it to accumulate in the body.
4. Hormonal Disorders and Endocrine Disruptors
✔ Hypogonadism (low testosterone production) leads to an imbalance between testosterone and estrogen, increasing the risk of gynecomastia.
✔ Endocrine disruptors (chemicals found in plastics, pesticides, and processed foods) can mimic estrogen and interfere with normal hormonal balance.
5. Medications That Increase Aromatase Activity
Certain drugs can increase aromatization or raise estrogen levels, including:
- Anabolic steroids (when discontinued, testosterone levels drop, and estrogen can dominate).
- Certain blood pressure medications (calcium channel blockers).
- Anti-anxiety and antidepressant drugs (SSRIs).
- Prostate cancer treatments (androgen deprivation therapy).
4. How to Reduce Aromatase Activity and Lower Estrogen Levels
1. Reduce Body Fat Through Diet and Exercise
✔ Weight loss lowers aromatase activity, reducing testosterone-to-estrogen conversion.
✔ Strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) help maintain a healthy testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
✔ Consuming a low-carb, high-protein diet can help regulate hormonal balance.
2. Optimize Liver Health for Estrogen Metabolism
✔ Limit alcohol consumption to avoid liver damage and impaired estrogen clearance.
✔ Eat cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, cauliflower) to support liver detoxification.
✔ Increase fiber intake to help eliminate excess estrogen through digestion.
3. Use Natural Aromatase Inhibitors
Certain natural compounds can help block aromatase activity and lower estrogen levels:
- Diindolylmethane (DIM) – Found in cruciferous vegetables, helps metabolize excess estrogen.
- Resveratrol – Found in red grapes, acts as a mild aromatase inhibitor.
- Zinc – Plays a role in testosterone production and inhibits aromatase.
4. Medications and Supplements That Block Aromatase
For severe cases of high estrogen and gynecomastia, doctors may prescribe aromatase inhibitors (AIs) such as:
- Anastrozole (Arimidex) – Blocks estrogen production.
- Letrozole (Femara) – More potent, used in certain medical conditions.
- Exemestane (Aromasin) – A steroidal aromatase inhibitor that permanently disables aromatase enzymes.
These medications are typically used in bodybuilders using anabolic steroids or men with hormone-related conditions, not as a general treatment for gynecomastia.
5. The Importance of Managing Aromatase Activity
Since high aromatase activity leads to increased estrogen levels, it is a significant factor in gynecomastia, fat gain, and testosterone suppression in men. By taking steps to reduce aromatase activity, such as losing weight, supporting liver health, using natural aromatase inhibitors, and considering medical treatment when necessary, men can restore hormonal balance and reduce the risk of male breast enlargement.
Treatment Options for Gynecomastia

Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies – Diet, Exercise, and Weight Loss Strategies
For men experiencing gynecomastia, making the right lifestyle changes can help reduce symptoms and restore hormonal balance naturally. Since gynecomastia is often linked to hormonal imbalances, obesity, and metabolic issues, incorporating diet, exercise, and weight management strategies can be a crucial step toward reversing or preventing male breast enlargement.
This section explores how lifestyle modifications—including nutrient-rich diets, strength training, fat loss strategies, and hormone-supporting foods—can help reduce the effects of gynecomastia naturally.
1. Diet for Hormonal Balance and Gynecomastia Reduction
Eating the right foods can help regulate testosterone and estrogen levels, reducing the likelihood of hormone-driven breast tissue growth. A gynecomastia-friendly diet focuses on foods that:
✔ Support testosterone production
✔ Reduce estrogen dominance
✔ Enhance fat metabolism
Foods That Support Testosterone and Reduce Estrogen
- Lean Proteins – Promote muscle growth and help regulate insulin levels.
- Examples: Chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, eggs, fish, tofu, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats – Essential for testosterone production and hormonal stability.
- Examples: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish (salmon, mackerel).
- Cruciferous Vegetables – Contain indole-3-carbinol (I3C), which helps the liver metabolize excess estrogen.
- Examples: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, kale, cauliflower, cabbage.
- Zinc-Rich Foods – Zinc is essential for testosterone production and reduces estrogen activity.
- Examples: Oysters, pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, cashews, and red meat.
- Foods High in Fiber – Helps detoxify excess estrogen through digestion.
- Examples: Whole grains, beans, flaxseeds, and fresh fruits.
Foods to Avoid
- Processed Foods and Sugary Snacks – Cause insulin resistance and promote estrogen dominance.
- Soy-Based Products – Contain phytoestrogens, which can mimic estrogen in the body.
- Alcohol – Affects liver function and reduces its ability to metabolize estrogen.
- Dairy with Added Hormones – Some dairy products contain synthetic hormones that may disrupt hormonal balance.
By eliminating estrogen-boosting foods and incorporating testosterone-supporting nutrients, men can naturally manage gynecomastia and maintain a healthy hormone balance.
2. Exercise Strategies to Reduce Gynecomastia
A targeted exercise plan can help burn fat, build muscle, and regulate testosterone levels, reducing the appearance of male breast enlargement. The two most effective forms of exercise for gynecomastia management are strength training and high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Strength Training for Testosterone Boosting
✔ Compound exercises – Multi-joint movements stimulate testosterone production and increase muscle mass.
✔ Focus on chest, shoulders, and arms – Building muscle in these areas reduces the appearance of enlarged breasts.
Best Strength Exercises for Gynecomastia:
- Bench Press (Flat, Incline, Decline) – Strengthens chest muscles.
- Push-Ups (Regular and Incline) – Tones the chest area.
- Dumbbell Flyes – Helps define pectoral muscles.
- Deadlifts and Squats – Boost overall testosterone levels.
Cardio and HIIT for Fat Loss
✔ HIIT workouts burn fat faster and increase testosterone more than traditional cardio.
✔ Helps reduce excess body fat, which lowers aromatase activity (the enzyme that converts testosterone to estrogen).
Example HIIT Workout (30 minutes):
- Jump Squats (45 seconds), Rest (15 seconds)
- Burpees (45 seconds), Rest (15 seconds)
- Push-Ups (45 seconds), Rest (15 seconds)
- Mountain Climbers (45 seconds), Rest (15 seconds)
- Kettlebell Swings (45 seconds), Rest (15 seconds)
✔ Repeat for 3-4 rounds
By combining strength training and HIIT, men can reduce fat deposits around the chest area and increase testosterone naturally, helping to reverse gynecomastia.
3. Weight Loss Strategies to Reduce Estrogen Dominance
Since excess body fat increases aromatase activity (which converts testosterone into estrogen), maintaining a healthy body weight is crucial for reducing gynecomastia symptoms.
1. Caloric Deficit for Fat Loss
✔ To lose weight, men should consume fewer calories than they burn daily.
✔ A combination of diet control and exercise creates a sustainable caloric deficit.
2. Intermittent Fasting for Hormonal Balance
✔ Fasting reduces insulin resistance, which helps regulate testosterone levels.
✔ Boosts growth hormone (GH) levels, which supports fat loss.
✔ Reduces estrogen dominance, as fasting enhances liver function for estrogen metabolism.
3. Hydration and Detoxification
✔ Drink plenty of water to aid in estrogen detoxification.
✔ Lemon water and green tea help cleanse the liver, promoting hormone balance.
By maintaining a healthy weight, men can lower estrogen levels, boost testosterone production, and reduce breast tissue growth, significantly improving gynecomastia symptoms.
By implementing these lifestyle changes—including a hormone-friendly diet, targeted exercise, and effective weight loss strategies—men can naturally reduce hormonal imbalances and manage gynecomastia without medical intervention
Medical Treatments and Hormone Therapy – Estrogen Blockers, Testosterone Therapy, and Medications
For men struggling with gynecomastia, lifestyle changes and natural remedies may not always be enough, especially if hormonal imbalances are severe or caused by underlying medical conditions. In such cases, medical treatments and hormone therapy can help restore the balance between testosterone and estrogen, reducing breast tissue growth.
There are three primary medical approaches to treating gynecomastia:
✔ Estrogen blockers (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators – SERMs)
✔ Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT)
✔ Medications that regulate hormones
Each treatment option is tailored to the individual’s condition, and a doctor’s evaluation is crucial before starting any therapy.
1. Estrogen Blockers (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators – SERMs)
Since high estrogen levels contribute to gynecomastia, medications that block estrogen activity can help reduce breast tissue growth. Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) work by preventing estrogen from binding to breast tissue receptors, thereby reducing its effects.
Common Estrogen Blockers for Gynecomastia
- Tamoxifen (Nolvadex)
✔ A widely used SERM that blocks estrogen receptors in breast tissue.
✔ Often prescribed for men with painful or severe gynecomastia.
✔ Helps reduce existing breast tissue growth and prevents further enlargement. - Raloxifene (Evista)
✔ Another SERM that helps reduce breast tissue growth in men.
✔ Often used for osteoporosis treatment, but also effective for hormonal gynecomastia.
Who Should Consider Estrogen Blockers?
✔ Men experiencing early-stage gynecomastia (within 1-2 years of development).
✔ Those who have high estrogen levels and low testosterone.
✔ Bodybuilders or steroid users experiencing hormone-related breast enlargement.
Note: SERMs do not significantly reduce body fat; they primarily work by limiting estrogen’s effect on breast tissue.
2. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
For men with low testosterone (hypogonadism), testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may help correct the hormonal imbalance that contributes to gynecomastia. Increasing testosterone levels can:
✔ Reduce estrogen dominance by maintaining the correct testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
✔ Suppress breast tissue growth in cases where low testosterone is the main cause of gynecomastia.
✔ Improve muscle mass, energy levels, and overall well-being.
Common Forms of Testosterone Therapy
- Testosterone Injections (Cypionate, Enanthate, Propionate)
✔ Delivered intramuscularly every 1-2 weeks.
✔ Provides consistent testosterone levels but requires regular injections. - Topical Testosterone Gels or Patches
✔ Applied daily to the skin.
✔ Provides steady testosterone absorption, but may increase estrogen conversion if not monitored properly. - Testosterone Pellets (Implants)
✔ Small pellets inserted under the skin that release testosterone gradually over 3-6 months.
When Is TRT Recommended?
✔ Men diagnosed with testosterone deficiency (hypogonadism).
✔ Those experiencing testosterone decline due to aging or medical conditions.
✔ Individuals with low testosterone-to-estrogen ratio contributing to gynecomastia.
Caution: In some cases, TRT can lead to increased estrogen conversion through aromatization (testosterone converting to estrogen), worsening gynecomastia. Doctors may prescribe aromatase inhibitors (AIs) alongside TRT to prevent this.
3. Medications That Regulate Hormones
In addition to SERMs and TRT, some hormone-regulating medications can help treat gynecomastia by either reducing estrogen production or blocking estrogen activity in the body.
1. Aromatase Inhibitors (AIs) – Blocking Testosterone-to-Estrogen Conversion
✔ Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) prevent the enzyme aromatase from converting testosterone into estrogen.
✔ This reduces estrogen levels, helping to prevent or shrink male breast tissue.
✔ Commonly used by bodybuilders or men with high estrogen production.
Common Aromatase Inhibitors for Gynecomastia:
✔ Anastrozole (Arimidex) – Often prescribed to men with high estrogen levels or steroid-induced gynecomastia.
✔ Letrozole (Femara) – A more potent AI used in advanced cases of estrogen dominance.
✔ Exemestane (Aromasin) – Helps reduce estrogen activity, though less commonly prescribed for gynecomastia.
2. Dopamine Agonists – Reducing Prolactin Levels
✔ Some cases of gynecomastia are caused by high prolactin levels (a hormone that stimulates breast tissue growth).
✔ Dopamine agonists like Cabergoline and Bromocriptine can help reduce prolactin levels, preventing gynecomastia caused by pituitary gland disorders.
4. When Is Surgery Needed?
If gynecomastia is severe, long-lasting, or unresponsive to medications, surgical removal may be the only effective treatment. Gynecomastia surgery typically includes:
✔ Liposuction – Removes excess fat deposits in the chest area.
✔ Glandular Tissue Excision – Removes fibrous breast tissue that cannot be eliminated through diet, exercise, or medication.
✔ Combination of Both – Many patients require both liposuction and tissue excision for optimal results.
Surgery is usually recommended for:
✔ Long-term gynecomastia (lasting over two years) where fibrous tissue has formed.
✔ Cases where hormone therapy and medications fail to produce results.
✔ Men experiencing significant psychological distress due to breast enlargement.
Final Thoughts on Medical Treatment for Gynecomastia
For men with hormone-related gynecomastia, medical treatments such as estrogen blockers, testosterone therapy, and hormone-regulating medications can help restore balance and reduce breast tissue growth. However, the best treatment approach depends on the underlying cause, so consulting a doctor or endocrinologist is essential before starting any therapy.
By addressing hormonal imbalances early, men can prevent gynecomastia from progressing and avoid the need for surgery in many cases
Surgical Procedures for Severe Cases – When Surgery (Liposuction or Mastectomy) Is Needed
For men with severe or persistent gynecomastia, where lifestyle changes, medications, or hormone therapy have failed to reduce breast tissue, surgical intervention may be the most effective solution. Gynecomastia surgery is a safe and well-established procedure that removes excess fat, glandular tissue, and sometimes skin to create a flatter, more masculine chest.
This section explores the different surgical options, who qualifies for surgery, and what to expect during the procedure and recovery process.
1. When Is Surgery Necessary?
While mild gynecomastia can often improve with weight loss and hormonal treatment, surgery becomes an option when:
✔ The condition has persisted for over two years despite medical treatment.
✔ Significant breast tissue growth is present and unresponsive to lifestyle changes.
✔ The breast tissue is fibrous and dense, making it difficult to reduce naturally.
✔ The individual experiences pain, tenderness, or discomfort due to the excess tissue.
✔ Gynecomastia causes psychological distress, low self-esteem, or social embarrassment.
✔ The patient is in good overall health and has stable hormone levels before surgery.
Surgical procedures for gynecomastia are customized to each patient based on the severity of breast enlargement, skin elasticity, and fat distribution.
2. Types of Gynecomastia Surgery
There are two main types of gynecomastia surgery, and some patients may require a combination of both for optimal results.
A. Liposuction – Removing Excess Fat Deposits
✔ Best for: Men with fatty gynecomastia (pseudogynecomastia) or mild cases of breast enlargement.
✔ Procedure: Removes excess fat from the chest through a small incision.
✔ Advantage: Minimally invasive, shorter recovery time, and less scarring than mastectomy.
How It Works:
- The surgeon makes small incisions (typically under the armpit or near the nipple).
- A thin cannula (tube) is inserted to break down and suction out fat cells.
- The chest is sculpted for a natural, masculine appearance.
💡 Note: Liposuction does not remove glandular tissue, so it is ineffective for men with true gynecomastia caused by hormonal imbalances.
B. Mastectomy – Removing Glandular Breast Tissue
✔ Best for: Men with firm, fibrous glandular tissue that cannot be removed through liposuction alone.
✔ Procedure: Removes glandular tissue and, in some cases, excess skin.
✔ Advantage: Permanently removes breast tissue, preventing gynecomastia from recurring.
How It Works:
- A small incision is made around the areola (periareolar incision) or under the chest fold.
- The glandular tissue is surgically excised while preserving natural chest contouring.
- The surgeon may also tighten skin and reposition the nipple if needed.
💡 Note: Mastectomy is more invasive than liposuction but is the only option for true gynecomastia.
C. Combination of Liposuction and Mastectomy
✔ Best for: Men with both excess fat and glandular tissue.
✔ Procedure: Liposuction removes fat, and mastectomy removes glandular tissue for a fully sculpted chest.
✔ Advantage: Provides the most comprehensive results for men with moderate to severe gynecomastia.
💡 Note: Some patients with loose or sagging skin may require skin removal or nipple repositioning for an improved cosmetic outcome.
3. What to Expect: Procedure, Recovery, and Results
A. The Surgical Procedure
✔ Performed under local anesthesia (with sedation) or general anesthesia.
✔ The procedure takes about 1-3 hours, depending on the severity of gynecomastia.
✔ The surgeon uses specialized techniques to ensure minimal scarring and a natural chest contour.
✔ Most gynecomastia surgeries are outpatient procedures, meaning the patient can go home the same day.
B. Recovery and Healing Process
✔ Compression Garments: Patients must wear a compression vest for 4-6 weeks to reduce swelling and support healing.
✔ Pain and Swelling: Mild bruising, soreness, and swelling are common for the first 1-2 weeks.
✔ Downtime: Most patients return to light daily activities within a few days and resume normal activities in 1-2 weeks.
✔ Exercise Restriction: Avoid intense workouts and heavy lifting for at least 4-6 weeks.
✔ Final Results: While initial improvements are visible within weeks, full results take 3-6 months as swelling subsides.
C. Risks and Considerations
Like any surgery, gynecomastia procedures come with some risks, including:
✔ Scarring (though usually minimal with skilled surgical techniques).
✔ Temporary numbness or sensitivity changes in the chest area.
✔ Asymmetry or irregular contours, which may require touch-up procedures.
✔ Fluid accumulation (seroma) or minor infections.
Choosing a board-certified plastic surgeon with experience in gynecomastia correction reduces the risk of complications and ensures optimal results.
4. Long-Term Results and Prevention
Gynecomastia surgery provides permanent results, but new fat deposits or hormone imbalances can cause recurrence if:
✔ Weight gain occurs, leading to fat accumulation in the chest.
✔ Anabolic steroids or estrogen-boosting medications are used post-surgery.
✔ Hormonal imbalances (testosterone decline, high estrogen) are not managed properly.
💡 Post-Surgery Tips:
✔ Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine to prevent fat accumulation.
✔ Avoid hormone-disrupting drugs and medications that can trigger gynecomastia.
✔ Have regular hormone check-ups to ensure testosterone and estrogen levels remain balanced.
Final Thoughts on Gynecomastia Surgery
Surgical intervention is a highly effective, long-term solution for men with severe or persistent gynecomastia. Whether through liposuction, mastectomy, or a combination of both, surgery removes excess breast tissue and restores a firmer, masculine chest.
For those struggling with self-esteem issues or physical discomfort, gynecomastia surgery can significantly improve confidence and quality of life. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and hormone balance is key to preventing recurrence after surgery.
Before considering surgery, it’s essential to consult a qualified plastic surgeon to determine the best treatment plan based on individual needs.
How to Prevent Hormonal Imbalances and Male Breast Growth

Maintaining a Healthy Hormone Balance – Nutrition, Exercise, and Avoiding Endocrine Disruptors
Achieving and maintaining hormonal balance is essential for preventing and managing gynecomastia. Since testosterone and estrogen levels play a crucial role in male breast tissue development, focusing on lifestyle factors such as nutrition, exercise, and reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors can help regulate hormones naturally.
This section explores how diet, physical activity, and environmental factors influence hormone health and what steps can be taken to support a balanced hormonal system.
1. Nutrition for Hormonal Balance
What you eat has a direct impact on hormone production and metabolism. A well-balanced diet that supports testosterone levels and reduces excess estrogen is crucial for maintaining healthy hormone levels and preventing the development of gynecomastia.
A. Foods That Boost Testosterone and Reduce Estrogen
Incorporating testosterone-boosting foods can help counteract hormonal imbalances:
✔ Healthy Fats – Omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated fats support testosterone production.
- Best sources: Olive oil, avocados, fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), nuts, and seeds.
✔ Lean Proteins – Helps build muscle and regulate hormones.
- Best sources: Eggs, chicken, turkey, grass-fed beef, and legumes.
✔ Cruciferous Vegetables – Contains compounds like indole-3-carbinol, which help the body metabolize excess estrogen.
- Best sources: Broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, and cabbage.
✔ Zinc-Rich Foods – Zinc is essential for testosterone production.
- Best sources: Oysters, shellfish, pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, and lentils.
✔ Vitamin D-Rich Foods – Supports healthy testosterone levels.
- Best sources: Egg yolks, salmon, sardines, and fortified dairy products.
✔ Herbs and Spices – Some natural herbs have been shown to boost testosterone.
- Best options: Ashwagandha, ginger, fenugreek, and turmeric.
B. Foods to Avoid (That Increase Estrogen or Lower Testosterone)
Some foods can increase estrogen levels or interfere with testosterone production, potentially worsening gynecomastia. Limiting or avoiding these foods can help maintain hormonal balance:
🚫 Processed and Sugary Foods – Excess sugar and refined carbs can lead to insulin resistance, which lowers testosterone.
- Examples: White bread, pastries, soda, candy, and processed snacks.
🚫 Alcohol – Particularly beer, as it contains phytoestrogens (plant-based estrogens) that can increase estrogen levels.
🚫 Soy-Based Products – Soy contains isoflavones, which mimic estrogen in the body.
- Examples: Soy milk, tofu, soy protein, and edamame.
🚫 Dairy Products – Some dairy products contain hormones that can disrupt testosterone balance.
🚫 High-Fat and Fried Foods – Can contribute to weight gain and hormonal imbalances.
2. Exercise for Hormonal Health
Regular physical activity plays a significant role in hormone regulation, weight management, and testosterone production. Incorporating strength training and cardiovascular exercises can help maintain a healthy body composition and reduce the risk of excess estrogen.
A. Strength Training and Resistance Exercises
✔ Increases testosterone levels naturally.
✔ Builds lean muscle mass, which helps regulate hormone balance.
✔ Boosts metabolism, helping to reduce fat storage (especially in the chest area).
💪 Best Strength Training Exercises:
- Squats and deadlifts – Work large muscle groups, leading to higher testosterone production.
- Bench presses and push-ups – Strengthen the chest muscles, improving chest definition.
- Pull-ups and rows – Help develop upper body strength and burn excess fat.
B. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
✔ Boosts testosterone and reduces cortisol (stress hormone).
✔ Increases fat-burning, which helps lower excess estrogen levels.
✔ Improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of hormonal imbalances.
🏃 Best HIIT Workouts:
- Sprint intervals (30 seconds sprint, 1-minute rest, repeat 8–10 times).
- Jump rope and burpees for full-body fat burning.
- Cycling sprints to engage lower body muscles.
C. Reducing Body Fat to Control Estrogen
✔ Excess fat tissue (especially belly fat) converts testosterone into estrogen through the enzyme aromatase.
✔ Losing weight through diet and exercise can naturally lower estrogen levels and prevent gynecomastia from worsening.
3. Avoiding Endocrine Disruptors
Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that interfere with the body’s natural hormone system, often leading to higher estrogen levels and lower testosterone levels. Reducing exposure to these harmful substances is essential for hormonal balance.
A. Common Endocrine Disruptors to Avoid
🚫 BPA (Bisphenol A) – Found in plastic bottles, food containers, and canned foods.
- Tip: Use glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic.
🚫 Phthalates – Found in some cosmetics, lotions, and plastic packaging.
- Tip: Choose natural personal care products without phthalates.
🚫 Pesticides and Herbicides – Found in conventionally grown fruits and vegetables.
- Tip: Opt for organic produce when possible.
🚫 Parabens – Found in shampoos, deodorants, and skincare products.
- Tip: Look for “paraben-free” products.
🚫 Soy-Based Products – Contains plant estrogens (phytoestrogens) that can increase estrogen levels.
B. Detoxifying the Body
To help eliminate stored endocrine disruptors, consider:
✔ Drinking plenty of water to flush out toxins.
✔ Eating fiber-rich foods to aid digestion and hormone regulation.
✔ Sweating through exercise or sauna therapy to remove toxins through the skin.
4. Managing Stress and Sleep for Hormonal Balance
A. Reducing Chronic Stress
✔ High cortisol (stress hormone) suppresses testosterone levels and can lead to hormonal imbalances.
✔ Stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help lower cortisol levels.
B. Prioritizing Quality Sleep
✔ Poor sleep reduces testosterone production, increasing the risk of hormonal imbalances.
✔ Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night.
✔ Follow a consistent sleep schedule to optimize hormone levels.
Final Thoughts on Maintaining Hormonal Balance
Balancing hormones naturally requires a combination of proper nutrition, regular exercise, and reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors. By incorporating testosterone-boosting foods, engaging in strength training, and avoiding hormone-disrupting chemicals, men can help regulate their hormonal health and reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
A holistic approach that includes healthy lifestyle habits, stress management, and proper sleep can optimize testosterone levels, prevent excess estrogen accumulation, and support long-term hormonal balance
Avoiding Medications That Affect Hormones – Being Aware of Drugs That Can Contribute to Gynecomastia
Certain medications can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to the development of gynecomastia by either increasing estrogen levels, decreasing testosterone, or directly stimulating breast tissue growth. Being aware of these drugs and discussing alternatives with a healthcare provider can help prevent or reduce the risk of gynecomastia.
1. Medications That Can Cause Gynecomastia
Several types of medications have been linked to hormonal imbalances that trigger male breast enlargement. Below are the most common culprits:
A. Anti-Androgen Medications (Testosterone Blockers)
✔ Purpose: Used to treat conditions like prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and hormonal disorders.
✔ Effect: These drugs block testosterone or increase estrogen activity, leading to breast tissue growth.
🔹 Common Examples:
- Finasteride (Propecia, Proscar) – Used for hair loss and prostate enlargement.
- Dutasteride (Avodart) – Treats BPH but can lower testosterone levels.
- Flutamide, Bicalutamide (Casodex) – Used for prostate cancer treatment.
🛑 Alternative Options:
- If treating hair loss, consider natural DHT blockers (like saw palmetto) instead of finasteride.
- If treating BPH, discuss non-hormonal treatments with a doctor.
B. Steroids and Hormonal Medications
✔ Purpose: Anabolic steroids are often used by bodybuilders and athletes to enhance muscle growth. Other hormonal drugs are used for medical conditions like testosterone deficiency.
✔ Effect: Some steroids convert into estrogen (via the aromatase enzyme), leading to breast enlargement in men.
🔹 Common Examples:
- Anabolic Steroids (Testosterone Injections, Trenbolone, Dianabol, Winstrol, etc.) – Increase muscle mass but can lead to testosterone-estrogen imbalance.
- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) – Can increase prolactin levels, stimulating breast tissue growth.
🛑 Alternative Options:
- For muscle building, focus on natural methods like high-protein diets and strength training.
- If testosterone replacement therapy is necessary, work with a doctor to monitor hormone levels and estrogen conversion.
C. Antidepressants and Anxiety Medications
✔ Purpose: Used to treat depression, anxiety, and mood disorders.
✔ Effect: Some of these medications alter hormone regulation by increasing prolactin or disrupting dopamine, which influences testosterone production.
🔹 Common Examples:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) – Like Fluoxetine (Prozac), Sertraline (Zoloft), and Paroxetine (Paxil).
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) – Like Amitriptyline and Clomipramine.
- Benzodiazepines – Like Diazepam (Valium) and Lorazepam (Ativan).
🛑 Alternative Options:
- Discuss lower-risk antidepressants with a doctor.
- Consider natural methods for mental health (exercise, therapy, or meditation).
D. Heart and Blood Pressure Medications
✔ Purpose: Used to treat high blood pressure, heart disease, and fluid retention.
✔ Effect: Some medications reduce testosterone levels or increase estrogen activity, causing gynecomastia.
🔹 Common Examples:
- Spironolactone (Aldactone) – A potassium-sparing diuretic that acts as a testosterone blocker.
- Calcium Channel Blockers – Like Amlodipine, Verapamil, and Diltiazem, which may affect hormone levels.
- ACE Inhibitors and Beta Blockers – Some beta-blockers (like Metoprolol, Atenolol) may contribute to hormonal imbalance.
🛑 Alternative Options:
- If on spironolactone, ask your doctor about alternative diuretics with less hormonal impact.
- Control blood pressure through diet, exercise, and stress management when possible.
E. Anti-Ulcer and Gastrointestinal Medications
✔ Purpose: Used for acid reflux, ulcers, and digestive disorders.
✔ Effect: Some medications increase prolactin levels, which can stimulate breast tissue growth.
🔹 Common Examples:
- Cimetidine (Tagamet) – A common acid reflux medication known to cause hormonal side effects.
- Omeprazole (Prilosec) and Ranitidine (Zantac) – May have minor effects on hormone regulation.
🛑 Alternative Options:
- Consider natural remedies for acid reflux (e.g., ginger, apple cider vinegar, probiotics).
- Choose newer acid reflux medications with fewer hormonal effects.
F. Antipsychotic and Epilepsy Medications
✔ Purpose: Used to manage schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and epilepsy.
✔ Effect: Many of these drugs increase prolactin, which stimulates breast growth in men.
🔹 Common Examples:
- Risperidone (Risperdal) – Strongly linked to gynecomastia due to prolactin increase.
- Haloperidol (Haldol) and Olanzapine (Zyprexa) – Affect dopamine, which influences testosterone regulation.
- Epilepsy Medications – Like Phenytoin (Dilantin) and Valproate, which may alter hormones.
🛑 Alternative Options:
- Ask about low-prolactin alternatives for antipsychotic medications.
- Monitor hormone levels if taking these drugs long-term.
2. How to Prevent Medication-Induced Gynecomastia
If you’re taking medications that may contribute to gynecomastia, consider the following steps:
✔ Talk to Your Doctor – If you’re on a medication that may cause gynecomastia, ask if alternative options are available.
✔ Monitor Hormone Levels – Regular blood tests can help track testosterone, estrogen, and prolactin levels to catch imbalances early.
✔ Lifestyle Adjustments – Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and reducing body fat can counteract some medication effects.
✔ Limit Medication Use When Possible – If a drug is not medically essential, consider discussing non-drug treatments or lifestyle modifications with your healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts on Avoiding Medications That Affect Hormones
Many common medications can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to gynecomastia. While some are necessary for treating medical conditions, there may be alternative options with fewer hormonal side effects.
By being aware of which drugs can increase estrogen, lower testosterone, or raise prolactin, you can work with your doctor to find safer alternatives and reduce the risk of medication-induced gynecomastia.
Regular Health Check-ups and Hormone Testing – The Importance of Monitoring Hormone Levels for Prevention
Regular health check-ups and hormone testing play a critical role in preventing, diagnosing, and managing gynecomastia. Since hormonal imbalances are the leading cause of male breast enlargement, tracking testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, and other key hormones can help identify problems before they lead to noticeable changes. By understanding hormone fluctuations early, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy balance and prevent excess breast tissue growth.
1. Why Regular Hormone Testing is Important
Hormonal imbalances can develop gradually over time due to aging, medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors. Without regular monitoring, these imbalances can go unnoticed until physical symptoms—such as gynecomastia, fatigue, low libido, or weight gain—become prominent.
✔ Early Detection – Identifying hormonal shifts early allows for timely intervention before gynecomastia progresses.
✔ Prevention of Severe Cases – Monitoring hormone levels can help prevent long-term breast tissue development, which may require surgery if untreated.
✔ Customized Treatment Plans – Regular tests help doctors tailor treatment strategies, whether through lifestyle changes, medications, or hormone therapy.
✔ Tracking Medication Side Effects – Certain drugs affect hormone levels, so testing helps determine if adjustments are needed.
2. Key Hormones to Monitor for Gynecomastia Prevention
Hormone testing typically involves blood tests that measure levels of androgens (male hormones), estrogens (female hormones), and other endocrine markers. Below are the most critical hormones linked to gynecomastia:
A. Testosterone (T) Levels
✔ Why It Matters: Testosterone is the primary male hormone responsible for muscle mass, libido, and masculine traits. Low testosterone (hypogonadism) can lead to breast tissue growth, fatigue, and weight gain.
✔ What to Watch For:
- Low testosterone (<300 ng/dL) may indicate hormonal imbalance.
- Testosterone-to-Estrogen Ratio – An imbalance between T and E2 (estradiol) can contribute to gynecomastia.
B. Estrogen (E2 – Estradiol) Levels
✔ Why It Matters: Estrogen is present in men in small amounts, but excessive levels can stimulate breast tissue development. High estrogen levels are a major contributor to gynecomastia.
✔ What to Watch For:
- Elevated estradiol (E2) (>40 pg/mL in men) is often linked to gynecomastia, mood changes, and fat accumulation.
- The Testosterone-to-Estrogen Ratio should remain balanced (typically >10:1 in men).
C. Prolactin Levels
✔ Why It Matters: Prolactin is a hormone that stimulates breast tissue growth and milk production in women. High prolactin levels in men can contribute to gynecomastia and low testosterone.
✔ What to Watch For:
- Normal range: 2–18 ng/mL (men).
- Elevated prolactin can result from medications, tumors (prolactinomas), or hypothyroidism.
D. LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone)
✔ Why It Matters: These hormones control testosterone production in the testes. Low levels indicate testicular dysfunction or pituitary gland issues.
✔ What to Watch For:
- Low LH/FSH may suggest hypogonadism (testosterone deficiency).
- Elevated LH with low testosterone could indicate testicular failure.
E. SHBG (Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin)
✔ Why It Matters: SHBG binds to testosterone and estrogen, affecting how much free hormone is available in the body.
✔ What to Watch For:
- High SHBG can lower free testosterone levels, increasing gynecomastia risk.
- Low SHBG may be linked to insulin resistance and obesity.
F. Thyroid Hormones (TSH, T3, T4)
✔ Why It Matters: Thyroid dysfunction can affect testosterone and estrogen metabolism. Hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) is linked to high prolactin levels and weight gain, which can increase gynecomastia risk.
✔ What to Watch For:
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone) levels – Elevated TSH may indicate hypothyroidism.
- Free T3 and Free T4 should be within normal ranges for proper metabolic function.
3. How Often Should Hormone Levels Be Checked?
✔ Routine Testing – Men at risk of gynecomastia should test hormone levels every 6-12 months.
✔ If Symptoms Appear – If breast enlargement, fatigue, or libido changes occur, immediate hormone testing is recommended.
✔ During Medication Use – If taking drugs that affect hormones (e.g., steroids, antidepressants, prostate medications), monitor levels regularly.
✔ Post-Treatment Follow-Ups – If undergoing hormone therapy or gynecomastia treatment, follow-ups help track progress and ensure hormonal stability.
4. How to Get Hormone Testing Done
There are several ways to check hormone levels:
🔹 Consult an Endocrinologist or Urologist – Specialists can order comprehensive hormone tests.
🔹 Routine Blood Tests at a Clinic or Lab – Most healthcare providers offer standard hormonal panels.
🔹 At-Home Testing Kits – Some companies provide at-home saliva or blood tests, though results should be confirmed with a doctor.
5. Lifestyle Adjustments to Maintain Healthy Hormones
Aside from regular testing, there are natural ways to maintain a hormonal balance and prevent gynecomastia:
✔ Eat a Nutrient-Dense Diet – Include healthy fats, lean proteins, and cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale) to support testosterone.
✔ Exercise Regularly – Strength training and high-intensity workouts help boost testosterone.
✔ Manage Stress – Chronic stress increases cortisol, which can lower testosterone.
✔ Avoid Endocrine Disruptors – Minimize exposure to BPA, parabens, and pesticides that mimic estrogen.
✔ Get Enough Sleep – Poor sleep lowers testosterone and raises stress hormones.
Final Thoughts on Regular Health Check-ups and Hormone Testing
Gynecomastia often results from hormonal imbalances, which can be prevented or managed with routine check-ups and hormone testing. By keeping track of testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, and other key hormones, men can take early action to prevent male breast enlargement before it becomes severe.
If you notice breast growth, fatigue, weight gain, or mood changes, getting comprehensive blood tests can help determine the underlying cause and guide the best treatment approach
Conclusion
Gynecomastia, or male breast enlargement, is often the result of hormonal imbalances, particularly when testosterone levels drop and estrogen levels rise. Factors such as aging, obesity, medical conditions, medications, and anabolic steroid use can all contribute to these hormonal shifts, leading to excess breast tissue growth.
Understanding the role of hormones like testosterone, estrogen, prolactin, and aromatase activity is crucial in identifying the root cause of gynecomastia. Fortunately, various treatment options are available, ranging from lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, and weight loss) to medical treatments like hormone therapy, estrogen blockers, and surgical interventions in severe cases.
Maintaining a healthy hormonal balance through regular health check-ups, proper nutrition, exercise, and avoiding endocrine disruptors can help prevent and manage gynecomastia. If you suspect hormonal imbalances are affecting you, seeking medical advice and hormone testing is the best step toward restoring balance and improving overall health